By Shem Jenkins
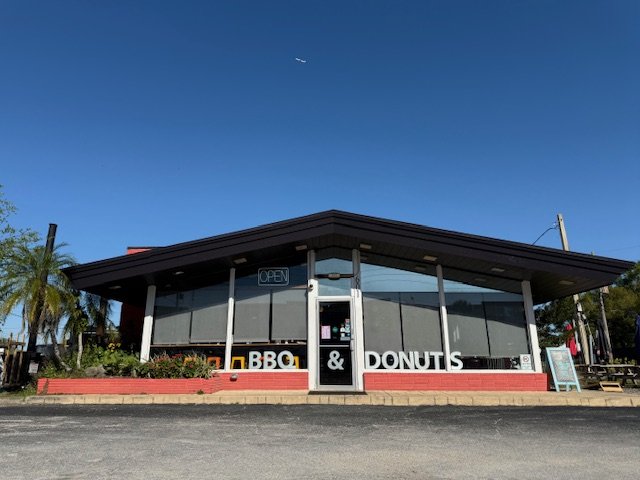
In the heart of Orlando's Milk District, Chef Ian Russell has carved out a niche with his unique culinary venture, Smoke & Donuts. This innovative restaurant, which combines the smoky flavors of barbecue with the sweet delight of donuts, has become a beloved local hot spot. But beyond the mouthwatering dishes, Chef Ian is making waves with his commitment to sustainability, particularly through his partnership with O-Town Compost.
The Birth of Smoke & Donuts - Chef Ian's culinary journey is as unique as is his restaurant. After high school, he embarked on a road trip across the United States, stopping at roadside BBQ joints in Texas, Tennessee, and the Carolinas. This journey ignited his passion for low and slow BBQ, which he later honed at The Culinary Institute of America in Hyde Park, New York, where he graduated in 2009.
Founded by Chef Ian and his wife Juliana, Smoke & Donuts began as a pop-up restaurant in 2017. The concept was simple yet ingenious: combine the savory goodness of barbecue with the irresistible charm of donuts. The pop-up, originally located in the back alley of Red Cypress Brewery, quickly gained popularity, evolving into a food truck in 2018 that found a semi-permanent home at à La Carte. Eventually, in February 2023, Smoke & Donuts opened their first brick-and-mortar location at the corner of N. Primrose Dr. and Fairgreen St., one-block south of E. Colonial Dr., in Orlando's Milk District.
Smoke & Donuts is a celebration of culinary artistry that blends innovative flavors with a deep commitment to the community and to the environment. Every element of the menu reflects Chef Ian’s philosophy that great food should be made well, with thought, attention and care, and accessible to everyone. Beyond the delicious offerings, Chef Ian is dedicated to making a difference in the way his restaurant runs and operates, particularly in terms of sustainability.
Embracing Sustainability with O-Town Compost - In recent years, recognizing the environmental impact of food waste, Chef Ian has taken his commitment to sustainability to the next level by partnering with O-Town Compost. This local composting service aims to reduce food waste by diverting it from the landfill and instead turning it into nutrient rich soil. This partnership has allowed Smoke & Donuts to compost food scraps, coffee grounds, and other organic materials, significantly reducing its overall waste footprint.
The decision to compost was not just about waste management for Chef Ian; it reflected his commitment to sustainability. By diverting organic waste from landfills, Smoke & Donuts is contributing to a circular economy, where waste is transformed into valuable resources. The compost produced from the restaurant’s scraps is used by local farmers and community gardeners to enrich their soil, growing more nutritious food, and creating a positive ripple effect in the community.
The Impact on Daily Operations - Implementing a composting program has transformed the operations at Smoke & Donuts. Chef Ian and his team have adopted new practices in the kitchen, focusing on minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency. This shift has led to a more mindful approach to sourcing ingredients, with an emphasis on local and sustainable products. By prioritizing local suppliers, Chef Ian not only supports the community but also reduces the carbon footprint associated with transporting food.
The composting initiative has also fostered a culture of sustainability among the staff. Team members are encouraged to think critically about waste and to find innovative solutions to reduce it. For instance, the cabbage left over from preparing coleslaw now finds new life in a tangy batch of homemade kimchi, and the smoked bones and trimmings from barbecue preparations are repurposed to create a savory, aromatic ramen broth. These practices represent Chef Ian’s holistic approach to sustainability - where every ingredient is utilized to its fullest potential. This collaborative effort has created a sense of pride within the team, as they work together towards a common goal of operating a responsible and eco-friendly restaurant.
Customer Engagement - The impact of Chef Ian’s commitment to sustainability extends beyond the kitchen. Customers at Smoke & Donuts are increasingly aware of the restaurant’s eco-friendly practices, and many appreciate the transparency surrounding the composting initiative. Chef Ian often shares insights about the importance of composting and sustainability through social media and in-person interactions, fostering a deeper connection with his patrons.
This engagement has resonated with customers, many of whom are eager to support businesses that prioritize environmental responsibility. As a result, Smoke & Donuts has cultivated a loyal customer base that values not only the delicious food but also the restaurant’s commitment to making a positive impact on the planet.
A Sustainable Future - Chef Ian has exciting plans to cultivate an herb garden on the side of Smoke & Donuts. With the help of O-Town Compost’s renowned Black Gold Compost, the garden will flourish, supplying fresh, aromatic herbs that promise to add another dimension of flavor to his dishes. This garden will become both a source of pride and sustainability, embodying the restaurant’s continuous journey towards greener practices.
Chef Ian’s journey from a pop-up to a thriving restaurant is a testament to his passion for food and his dedication to sustainability. By partnering with O-Town Compost, he has taken significant steps towards reducing waste and promoting eco-friendly practices in the restaurant industry. As Smoke & Donuts continues to grow, Chef Ian remains committed to operating a sustainable restaurant that not only serves delicious food but also contributes to a healthier planet.
Looking ahead, Chef Ian hopes to continue expanding Smoke & Donuts' sustainability efforts and is constantly looking for new ways to reduce their environmental impact, whether it’s through composting, sourcing locally grown ingredients and supplies, or creating tasty additions to the menu by rethinking how every part of ingredients could be used.
In a world where sustainability is becoming increasingly important, Chef Ian stands out as a leader in the culinary community. His innovative approach to cooking, composting and waste management is inspiring other restaurateurs to follow suit, proving that it is possible to create a successful business while prioritizing the environment. Through their partnership with O-Town Compost and their dedication to eco-friendly practices, they are proving that delicious food and environmental responsibility can go hand in hand.